- KDDI HOME
 Corporate Information
Corporate Information  About KDDI
About KDDI  Released Information
Released Information  Security Portal
Security Portal  Smartphone Security Measures
Smartphone Security Measures
Smartphone Security Measures


Contents
 Keeping your smartphone updated
Keeping your smartphone updated Do not install unauthorized apps―Protect your smartphone from malware and viruses
Do not install unauthorized apps―Protect your smartphone from malware and viruses Using a safer authentication method
Using a safer authentication method Preparing for loss and theft
Preparing for loss and theft Taking precautions against phishing
Taking precautions against phishing Using Wi-Fi carefully
Using Wi-Fi carefully Checking how your privacy information is used
Checking how your privacy information is used Using security software
Using security software Useful information
Useful information
KDDI recommends precautions and security measures for customers to help you avoid falling victim to cybercrime.
Keeping your smartphone updated
Your smartphone is a useful tool that enables you to connect to the Internet like a computer to view various websites and videos, and install different apps for use.
On the other side of its usefulness, smartphones are also not free from virus infections and attacks targeting software vulnerabilities just like computers. Keep the OS and apps on your smartphone updated to the latest versions to protect them from such attacks.
Updating the OS
Android smartphones and iPhones offer new functional additions, bug fixes, and patches for newly discovered vulnerabilities as OS updates and security function improvements (collectively "Updates").
When an OS update for your smartphone is available, you will see an OS update notification displayed on your smartphone. Make sure to run OS updates.
See below for OS update information for Android smartphones.
- au
 Product update information list (in Japanese only)
Product update information list (in Japanese only) - UQ mobile
 What's new (in Japanese only)
What's new (in Japanese only) - Other than the above
Visit the respective websites of your telecommunications carrier or device manufacturer.
Visit the ![]() Apple Inc. website (in Japanese only) for OS update information for iPhones.
Apple Inc. website (in Japanese only) for OS update information for iPhones.
Updating Apps
For smartphone apps, you may need to apply security patches to protect against vulnerabilities in addition to updating the app for new functional additions and/or bug fixes. Likewise the OS, keep your apps updated to their latest versions. It is also useful to set up automatic updates for apps in the OS settings so that apps will be automatically updated.
For instructions on how to set up automatic updates, visit the respective Web pages provided by ![]() Google (in Japanese only) for Android smartphones and by
Google (in Japanese only) for Android smartphones and by ![]() Apple Inc. (in Japanese only) for iPhones. Setting automatic updates for apps may incur communications fee with each update. If you are concerned about communications fees, it is recommended that you set up your automatic app updates to only take place while connected to a Wi-Fi network.
Apple Inc. (in Japanese only) for iPhones. Setting automatic updates for apps may incur communications fee with each update. If you are concerned about communications fees, it is recommended that you set up your automatic app updates to only take place while connected to a Wi-Fi network.
Do not install unauthorized apps―Protect your smartphone from malware and viruses
There is an increasing number of cases where scammers try to lure you into installing malware, guided from fake warnings that appear in phishing and smishing messages or on websites. Once you install malware, you may end up having information on your smartphone stolen or making payments that you never made yourself. To keep your smartphone protected from such danger, do not install any suspicious apps.
Do not install apps from unknown sources (Only install apps from official markets)
On Android smartphones, you can install apps from providers other than the Play store (Google Play) and other carrier-provided official markets. These unknown apps, or apps from unknown sources, may not be sufficiently verified to be safe, and therefore as a general rule, you should not install such apps.
Android smartphones are initially set to block installations of unknown apps or apps from unknown sources. When you attempt to install such an app, a warning will be displayed. You can still install such apps by allowing installation of apps from unknown sources or apps from a particular source, but this setting does not need to be turned on for normal use.
Keep this setting turned off unless you are completely aware of the risks.

On another note, while it is possible for you to click an app file (APK file) attached to a message and install it on your Android smartphone, generally APK files are not attached and sent via emails. In most cases, they contain malware. You should ignore such messages from unknown senders, but even messages from people you known can be impersonated. Unless you can be sure that such files are safe by checking with the sender in person or over phone, it is better not to install such attachments.
Using a safer authentication method
Reports have been made about damage caused by unauthorized logins to online services resulting in theft of money and personal and other important information.
In addition to conventional brute-force attacks and dictionary attacks, we are seeing schemes that involve theft of passwords or even two-factor authentication codes by a phishing scam in recent years.
It is important to step up authentication for accessing services in order to protect yourself from such shrewd attacks.
Using biometric authentication
Biometric authentication using fingerprints and face recognition is a safer alternative authentication method to authentications using a login ID and password. Not using a password simply reduces the risk of unauthorized login by a third party that steals passwords from phishing sites. Active use of biometric authentication is recommended when using services that offer biometric authentication.
KDDI's "login by fingerprint and face recognition" uses the smartphone's device lock function. Use a PIN code for device lock that cannot be guessed easily so that you can protect your smartphone in the event of theft or loss.
Information generated in the device for biometric authentication (called "private key") is also shared with Google Password Manager and iCloud Keychain, which means that once your Google account or Apple ID is compromised, all of the services that you have set up biometric authentication for can suffer unauthorized access. Be careful about how you manage login information (including passwords and secret questions) of management services that share a private key.
Using authentication apps
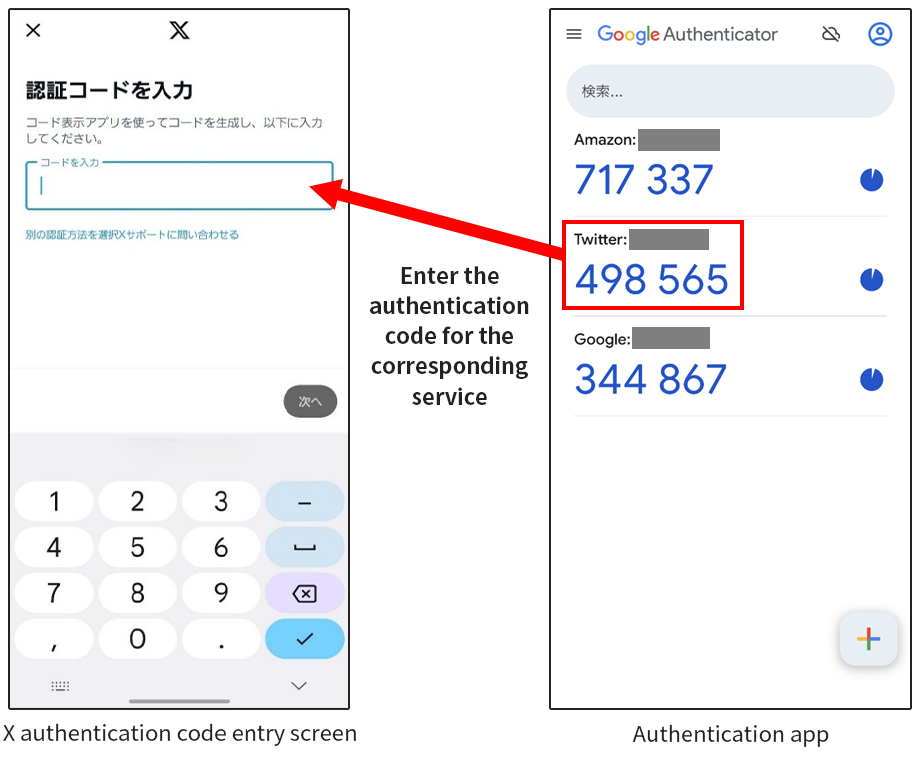
For some services, you can achieve secure authentication by using an authentication app.
Authentication apps are generally used as additional login authentication. As authentication apps use a smartphone-generated authentication code that is only valid for a short period of time, there is little concern for password peeping or interception and you can securely log in.
However, you need to keep in mind that, for services that use emails or SMS for resetting the authentication app, there is still a risk of a third party resetting the authentication if your email account is taken over or your SMS is intercepted.
When you set up an authentication app to be used for a service, you are prompted to enter an authentication code after entering your login ID and password. You then check your authentication app for the authentication code and enter that code to log into the service.
Examples of such authentication apps are Google's Authenticator app and Microsoft's Authenticator app. While iOS (iPhone) does not have such apps, it provides a password management function that you can access from Settings - Password.
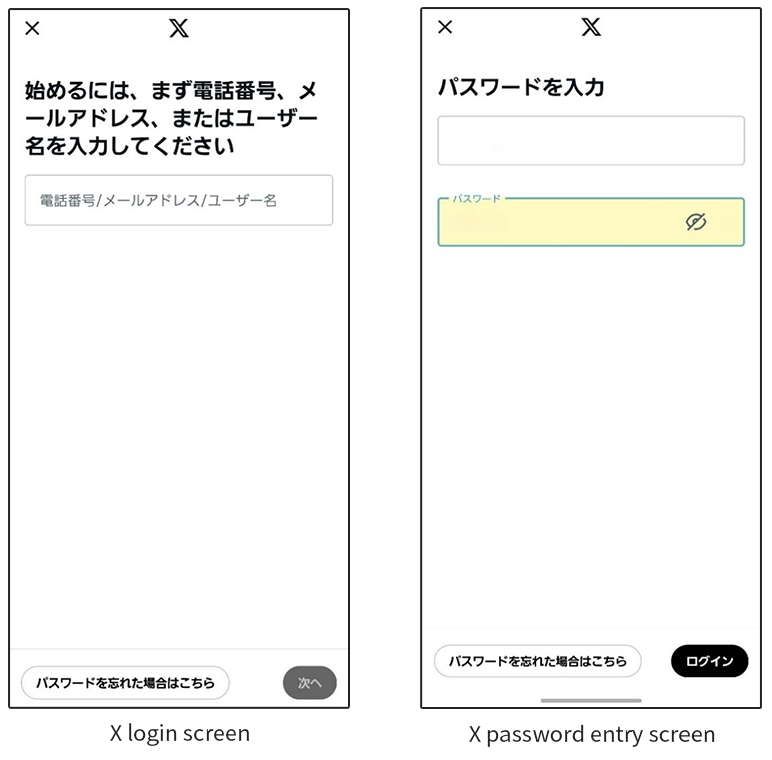
Authentication on X
Using the password management app
You can use a password management app that is installed separately from the services that you are using.
By using a password management app, your device can identify the URL of the website of the service and automatically enter the corresponding ID and password. This saves you from needing to remember the password, which makes it easier for you to use more complex, safer passwords.
Additionally, this allows you to notice that something is wrong when the automatic password entry is not working. If automatic password entry does not work on a website that appears to be the one that you are familiar with, you can suspect that it may be a cunningly disguised phishing site.
A password management app is also available from au.
This is also available to UQ mobile and povo users by subscribing to au Smart Pass Premium.
 Password management: Data storage (For au users) (in Japanese only)
Password management: Data storage (For au users) (in Japanese only) Data storage (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only)
Data storage (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only)
Setting a stronger password
Using simple passwords creates an increased risk of unauthorized access by brute-force attacks or dictionary attacks.
Even when you are using a complex password, if you are sharing it with other websites and it leaks from one of them, it is no longer safe to use.
To ensure password security, it is important to set a strong password and not share one password across multiple websites.
Since remembering all of your passwords can be difficult, consider using a password management app as mentioned above.
Preparing for loss and theft
Smartphones tend to carry important information, and in case they are lost or stolen, the important information may be disclosed or wrongfully used. We provide the information below to deal with such circumstances.
If you have lost your smartphone or had it stolen, use the following links as reference to take action.
 If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For au users) (in Japanese only)
If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For au users) (in Japanese only) Lost or stolen smartphone (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only)
Lost or stolen smartphone (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only) If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For povo 2.0 users) (in Japanese only)
If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For povo 2.0 users) (in Japanese only) If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For povo 1.0 users) (in Japanese only)
If your smartphone is lost or stolen (For povo 1.0 users) (in Japanese only)
Screen lock
Set a screen lock when you purchase a smartphone. A screen lock can reduce the risk of someone else seeing the information in your smartphone in case you misplace your smartphone.
Remote support function (remote lock and location search)
A remote lock function and location search function are provided as preparation in case your smartphone is lost or stolen. Setting these functions in advance is recommended. With these functions, you can remotely lock your smartphone and/or delete data on your smartphone to prevent information leaks in case of loss or theft.
Device data backup
If your smartphone is lost or stolen, you may lose important information saved on your smartphone. There may be cases where you have to delete data on your smartphone using the remote support function to avoid leakage of important information.
It is recommended that you make a backup of your smartphone data so that you can recover data later even if you end up losing the data on your smartphone.
au provides a data storage service that saves the photos, contacts, and other important data saved on your smartphone to au's servers.
This is also available to UQ mobile and povo users by subscribing to au Smart Pass Premium.
![]() Data storage (in Japanese only)
Data storage (in Japanese only)
Taking precautions against phishing
Click the link below for information about phishing.
![]() To protect yourself from falling victim to phishing (in Japanese only)
To protect yourself from falling victim to phishing (in Japanese only)
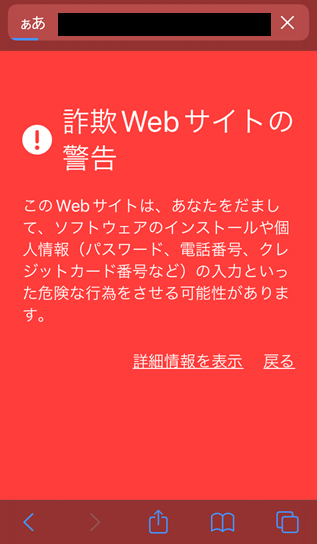
Taking precautions against Web browser warnings
A Web browser may display a warning screen when you access unsafe websites such as phishing websites. If a warning screen is displayed, close the browser page and do not access that site.
Users are not warned on all unsafe websites, so you cannot be too careful even when a warning screen is not displayed.

Taking precautions against fake warnings
While browsing websites, you may suddenly see a warning message like "Warning―Your Computer Is Infected!" pop up on the screen. This is a fake message intended to redirect you to a page that prompts you to install a malicious app or provide your personal information. When you see this kind of display, close the page and do not further access the page.

Taking precautions against shortened URLs
In SNS, SMS, and emails, sometimes a shortened URL link called short URLs may be used to work around lengthy text size and the resulting reduced readability when the full URL is included.
By clicking the short URL, you will be directed to the intended website, which means that you cannot tell from the short URL which website you will be accessing.
An attacker often takes advantage of this function to direct you to phishing and fraud websites. Therefore, try not to casually access links in SMS and emails that you are unsure of.
It is recommended that you bookmark the official websites of services you use and access the websites from the bookmarks.

Using Wi-Fi carefully
While public Wi-Fi is freely accessible by anyone, there are Wi-Fi networks that are not sufficiently secure or are set up with the intention to harm users. Therefore, it is important to use public Wi-Fi upon confirming its safety.
Using Wi-Fi services provided by telecom carriers
You can safely use Wi-Fi by connecting to a Wi-Fi service provided by a telecom carrier.
au provides Wi-Fi services at stations and cafés.
 au Wi-Fi SPOT (For au users) (in Japanese only)
au Wi-Fi SPOT (For au users) (in Japanese only) au Wi-Fi Access (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only) Use of au PAY is required.
au Wi-Fi Access (For UQ mobile/povo users) (in Japanese only) Use of au PAY is required.
Using the VPN function
With public Wi-Fi, many people share the Wi-Fi-network to connect to the Internet. Therefore, a Wi-Fi network without sufficient security leaves a chance of having your transmitted or received data tapped by a third party. As an approach to use Wi-Fi networks safely even in such environments, you can use a VPN to protect your communications. When using a VPN, communications take place over a virtual dedicated network, which prevents data tapping by a third party.
![]() au Wi-Fi Access (in Japanese only) provides a security mode that offers a VPN when using a Wi-Fi service.
au Wi-Fi Access (in Japanese only) provides a security mode that offers a VPN when using a Wi-Fi service.

Checking how your privacy information is used
Many smartphone apps collect necessary information during your app use. On the other hand, some apps also collect unnecessary data, which is considered questionable from the user privacy perspective.
When you start an app for the first time, you are shown its terms of use and privacy policy to which you are asked to agree regarding the collection of information from your smartphone. Check for any unnecessary data collection.
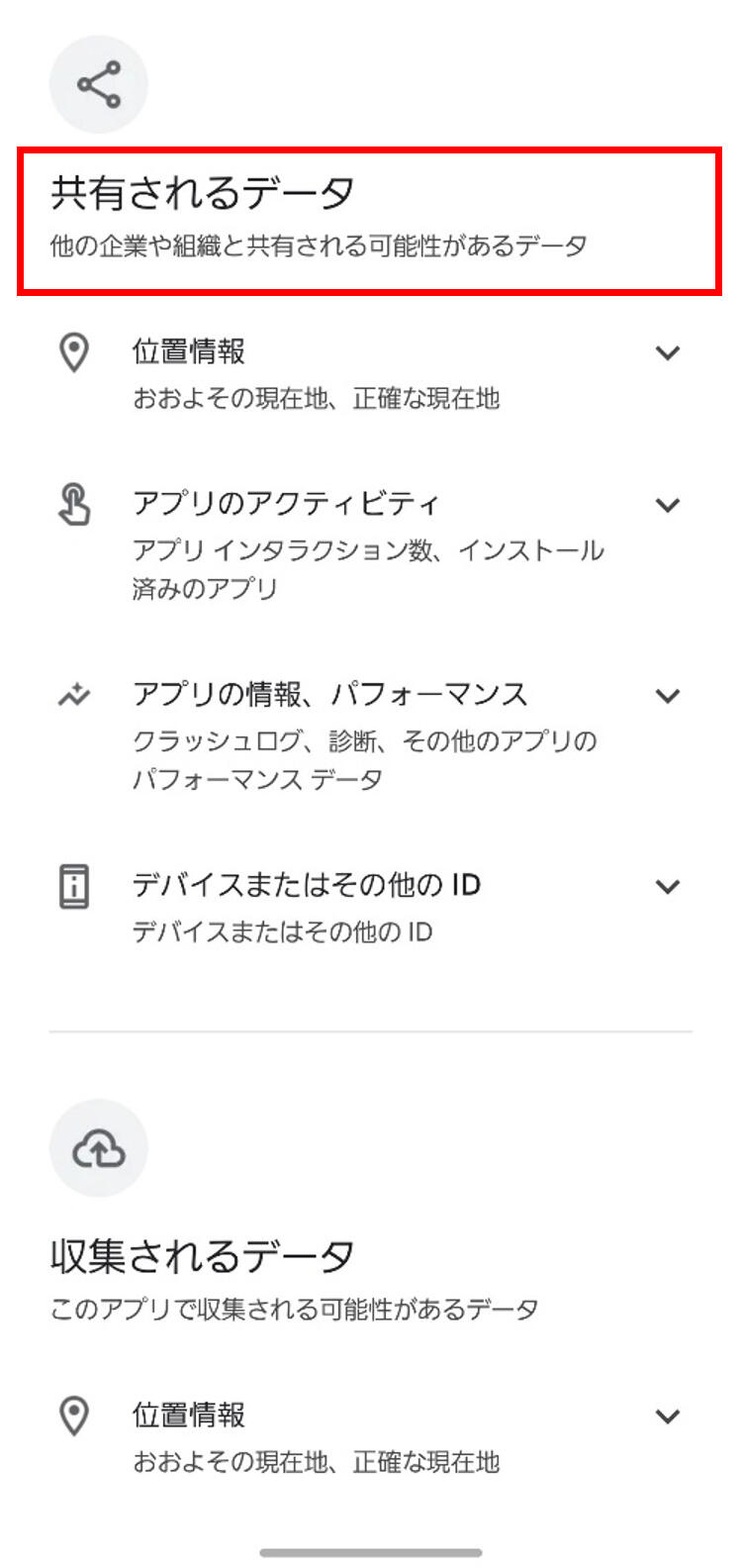
Both on App Store and Google Play, the app download pages display an explanation of what data is handled on the app, so it is better to check this information before downloading an app. If the app handles data that does not seem necessary for using the app, it is possible that the app is collecting data inappropriately. In such a case, you should either stop using the app, or if you are continuing use, take appropriate caution during use such as not agreeing to unnecessary permissions.
Checking the privacy information on iPhone apps
When downloading an app from App Store, you will see "App Privacy" displayed at the bottom of the app download screen, and by tapping [See Details], you can view what kind of data that app may handle.

Checking the privacy information on Android apps
When downloading an app from Google Play, you will see "Data Safety" displayed at the bottom of the app download screen, and by tapping [See details], you can view what kind of data that app shares and collects.
Using security software
As detailed below, security software offers a variety of security measures.
Protecting against malware
This function protects your smartphone from installing malware from email attachments and phishing and other dangerous websites.
However, security software is not a be-all-end-all solution and cannot defend against all dangers. Do not put excessive trust in security software-simply avoid accessing suspicious websites.
Protecting against unauthorized Wi-Fi connection
This function detects dangerous Wi-Fi networks and stops your smartphone from connecting to detected dangerous networks.
In some cases, this function may come with a function that performs VPN connection for Wi-Fi connections. For a detailed explanation of VPN connections, see "Using Wi-Fi carefully."
Protecting against unauthorized Web access
This function detects phishing and other malicious websites and displays a warning similar to a warning screen on a Web browser, preventing you from accessing such websites when you make an attempt. This function prevents unauthorized access based on the security software company's information.
Likewise the warnings in Web browsers, users are not warned on all unsafe websites, so you cannot be too careful even when a warning screen is not displayed.
Dark Web monitoring function
Dark Web refers to a part of the World Wide Web that is "underground" and cannot be searched by normal search engines. On the dark Web, cyber-criminals trade personal information such as email addresses, and the dark Web monitoring function checks whether the user's personal information is being traded on the dark Web.
Since different types of security software support different functions, it is necessary to thoroughly check what functions you need before making a selection. Some products are also provided combined with computer security software, which is another option that you can select according to your usage needs.
KDDI offers security software at au Style/au shops.
It can also be purchased at the au Online Shop (see sales page for sales conditions, etc.).![]() au Online Shop (in Japanese only)
au Online Shop (in Japanese only)
In addition, if you are using an Android smartphone, you can subscribe to au Smart Pass Premium to use Virus Block, which prevents virus infection.![]() Virus Block (in Japanese only)
Virus Block (in Japanese only)
Useful information
-

Watch for SNS account hacking! Introducing the latest tactics on Twitter and how to check for and prevent account hacking (in Japanese only)

2021.09.15
-

What is smishing that takes advantage of delivery attempt notifications? Protective measures and the latest cases explained (in Japanese only)

2021.08.10
-

What is the difference between OS updates and software updates? Update types and precautions explained (in Japanese only)

2021.05.26
-

What is a fake alert fraud? The latest cases, including calendar misapplication, and protective measures explained (in Japanese only)

2021.05.14
-

What are some anti-virus protections for iPhones? Circumstances around smartphone protection and quick-and-easy infection prevention measures explained (in Japanese only)

2020.06.29
-

What happens when you don't update your Android smartphone? Introducing benefits, precautions, and smart ways to update your smartphone (in Japanese only)

2020.02.20
-

Smart way to find your Android smartphone! How to use and set this function explained (in Japanese only)

2019.04.08
-

au's Data Storage app is useful for creating a data backup and managing passwords on your smartphone (in Japanese only)

2019.03.07
-

What is malware? Differences from viruses, types, and how to protect your smartphone from being infected by malware explained (in Japanese only)

2019.01.24
-

VPN: The linchpin of security in the public Wi-Fi age. Its safety and how to use it on a smartphone (in Japanese only)

2018.08.21